Mer/Build/UsingGitorious
(Merging glib example) |
(→Handling new upstream) |
||
| Line 252: | Line 252: | ||
git push --all | git push --all | ||
git push --tags | git push --tags | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
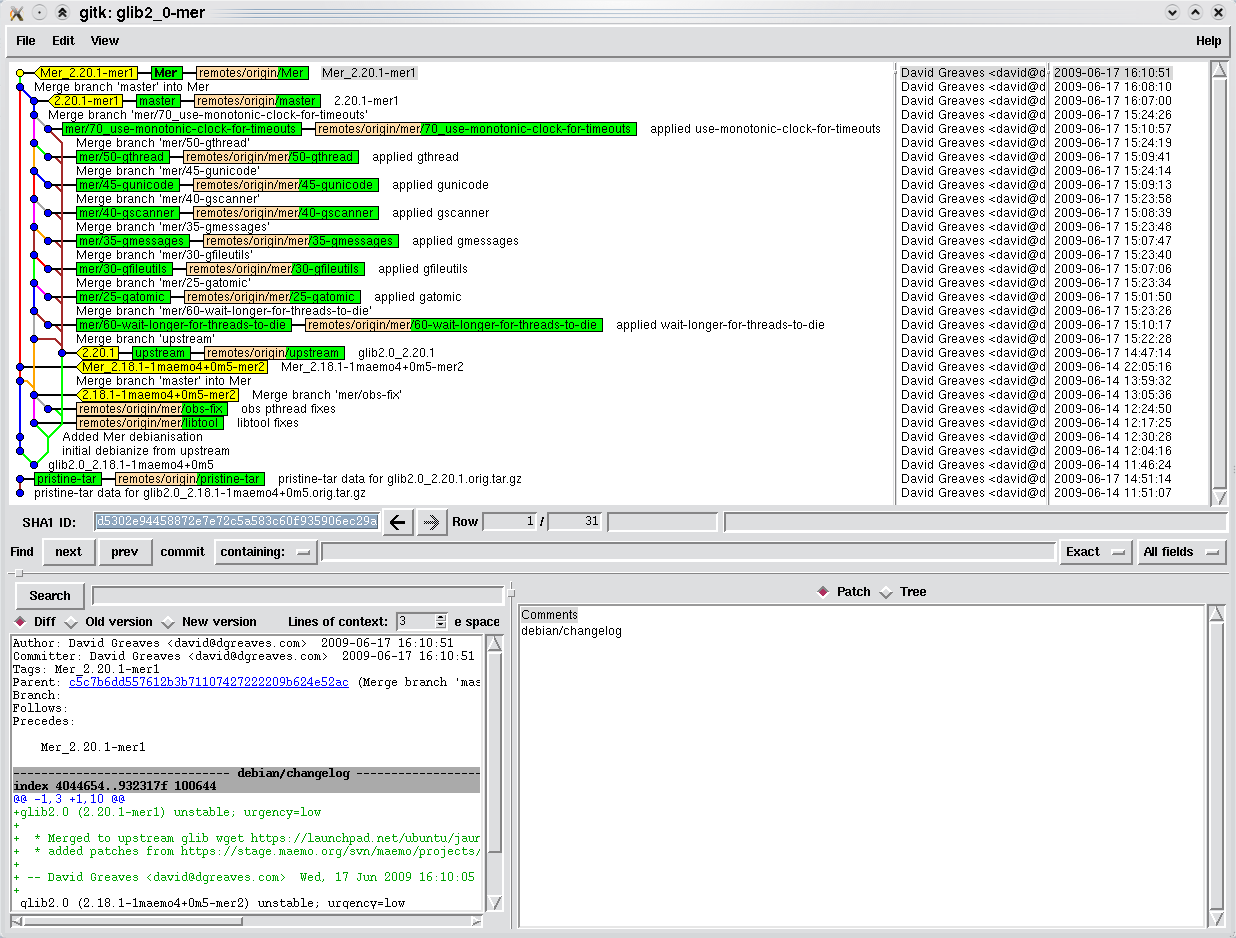
| + | The resultant merge looks like this : | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Mer-lbt-gitk-glib.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Read upwards to progress in time. Note how on the right is the 'upstream' branch tagged at 2.20.1 then you see the Mer patches being applied to master which is then merged into Mer. | ||
| + | (There is slight complexity here since the upstream changed to the *real* upstream). | ||
== Working from Gitorious == | == Working from Gitorious == | ||
Revision as of 15:22, 17 June 2009
Contents |
Packaging
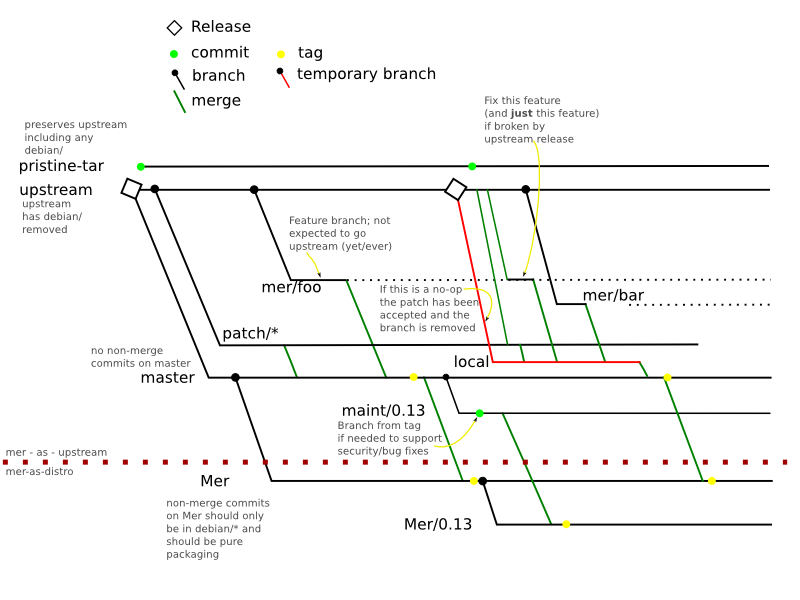
The Mer DVCS packaging process looks like this:
An upstream package is unpacked and the debian/ directory is removed.
It is then commited onto the upstream branch.
pristine-tar is used to ensure that the upstream tarball can be recreated perfectly.
master is the main branch and the only non-merge commits directly on this branch should be packaging-based and in debian/
All features or bug fixes are broken out to additional branches; 1 branch per feature or fix. The main difference is that features are not likely to go upstream whilst fixes are. This is very similar to quilt.
Developing
Development of a feature is done by cloning master; then branching locally and developing against master.
Once development is complete a new feature branch is created and the development branch is then cherry-picked onto the new feature branch.
Moving a Package to Gitorious
Initial setup
The following scripts need:
PKG=<package name> GPKG=<gitorious-safe package name> (ie [a-z0-9_-] UPVER=<upstream version> TARBALL=<tarball name> TAG=<new version>
Get the upstream source unpacked
mkdir $PKG cd $PKG mkdir _tmp cd _tmp tar xf ../../$TARBALL mv */* ../ cd .. rm -rf _tmp
Cleanse the install
mv debian ..
Create a git repo with the new stuff
git init
git add .
git commit -am"${PKG}_$UPVER"
This is really the upstream branch
git branch -m master upstream
For keeping an eye on things you may want gitk running. Use File->reload frequently (F5 doesn't work for me)
gitk --all &
Save state
pristine-tar commit ../$TARBALL
Prepare structure create master branch from upstream
git checkout -b master
create Mer branch from master
git checkout -b Mer
Apply debianisation
mv ../debian . git add debian/ git commit -am "initial debianize from upstream"
Feature/patch branches
Now apply features from the .diff.gz this has to be done manually
Identify a libtool feature
git checkout upstream git checkout -b mer/libtool
apply hunks
git commit -am"libtool fixes"
Identify an obs-fix feature
git checkout upstream git checkout -b mer/obs-fix
apply hunks
git commit -am"obs pthread fixes"
Now any debian/ hunks
git checkout Mer
apply hunks
git commit -am"Added Mer debianisation"
Now pull it all together
git checkout master
look for all the mer/* and patch/* branches and merge them
git branch -l git merge mer/libtool git merge mer/obs-fix
now use git log to create a top level ChangeLog entry
git add ChangeLog git commit -m"$TAG"
Mark an 'upstream' release
git tag $TAG
Now make a distro release
git checkout Mer git merge master
now use git log to create a debian/changelog entry
git add debian/changelog git commit -m"Mer_$TAG" git tag Mer_$TAG
Verify
Remove all obs code:
cd .. rm $PKG*
regenerate it:
cd $PKG pristine-tar checkout ../$TARBALL debuild -S -i.git
Build or examine to verify
Push
Now push to gitorious
git symbolic-ref HEAD refs/heads/Mer
Logon to http://gitorious.org/mer and create gitorious project
git remote add origin git@gitorious.org:mer/$GPKG.git git push --mirror origin
on gitorious goto 'Edit Repository' and set default to Mer
Handling new upstream
This shows by example how glib upstream was merged.
Clone the gitorious repository (I made a clone on gitorious first) at git@gitorious.org:~lbt/mer/glib2_0-mer.git
http://gitorious.org/~lbt/mer/glib2_0-mer
Get new upstream
wget https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/jaunty/+source/glib2.0/2.20.1-0ubuntu2/+files/glib2.0_2.20.1.orig.tar.gz TARBALL=glib2.0_2.20.1.orig.tar.gz mkdir ../patches cd ../patches/ wget https://stage.maemo.org/svn/maemo/projects/haf/branches/glib/glib-2-20/debian/patches/25-gatomic.patch wget https://stage.maemo.org/svn/maemo/projects/haf/branches/glib/glib-2-20/debian/patches/30-gfileutils.patch wget https://stage.maemo.org/svn/maemo/projects/haf/branches/glib/glib-2-20/debian/patches/35-gmessages.patch wget https://stage.maemo.org/svn/maemo/projects/haf/branches/glib/glib-2-20/debian/patches/40-gscanner.patch wget https://stage.maemo.org/svn/maemo/projects/haf/branches/glib/glib-2-20/debian/patches/45-gunicode.patch wget https://stage.maemo.org/svn/maemo/projects/haf/branches/glib/glib-2-20/debian/patches/50-gthread.patch wget https://stage.maemo.org/svn/maemo/projects/haf/branches/glib/glib-2-20/debian/patches/60_wait-longer-for-threads-to-die.patch wget https://stage.maemo.org/svn/maemo/projects/haf/branches/glib/glib-2-20/debian/patches/70_use-monotonic-clock-for-timeouts.patch wget https://stage.maemo.org/svn/maemo/projects/haf/branches/glib/glib-2-20/debian/patches/series
Prepare to merge
git clone git@gitorious.org:~lbt/mer/glib2_0-mer.git cd glib2_0-mer/ git checkout --track origin/upstream git rm -r *
replace the upstream code
mkdir _tmp cd _tmp tar xf ../../$TARBALL mv */* ../ cd .. rm -rf _tmp git add .
Now we have a clean upstream release
git commit -am"glib2.0_2.20.1" git tag 2.20.1 pristine-tar commit ../glib2.0_2.20.1.orig.tar.gz
Apply all the maemo patches to their own branches
git checkout upstream;git checkout -b mer/25-gatomic patch -p1 < ../patches/25-gatomic.patch git commit -am"applied gatomic"
git checkout upstream;git checkout -b mer/30-gfileutils patch -p1 < ../patches/30-gfileutils.patch git commit -am"applied gfileutils"
git checkout upstream;git checkout -b mer/35-gmessages patch -p1 < ../patches/35-gmessages.patch git commit -am"applied gmessages"
git checkout upstream ;git checkout -b mer/40-gscanner patch -p1 < ../patches/40-gscanner.patch git commit -am"applied gscanner"
git checkout upstream ;git checkout -b mer/45-gunicode patch -p1 < ../patches/45-gunicode.patch git commit -am"applied gunicode"
git checkout upstream ;git checkout -b mer/50-gthread patch -p1 < ../patches/50-gthread.patch git commit -am"applied gthread"
git checkout upstream ;git checkout -b mer/60-wait-longer-for-threads-to-die patch -p1 < ../patches/60_wait-longer-for-threads-to-die.patch git commit -am"applied wait-longer-for-threads-to-die" git checkout upstream ;git checkout -b mer/70_use-monotonic-clock-for-timeouts patch -p1 < ../patches/70_use-monotonic-clock-for-timeouts.patch git commit -am"applied use-monotonic-clock-for-timeouts"
Now to create a Mer glib from a master
git checkout --track origin/master
Upgrade entire glib
git merge upstream
Now we apply in series order.. feel free to do this in different orders
git merge mer/60-wait-longer-for-threads-to-die git merge mer/25-gatomic git merge mer/30-gfileutils git merge mer/35-gmessages git merge mer/40-gscanner git merge mer/45-gunicode git merge mer/50-gthread git merge mer/70_use-monotonic-clock-for-timeouts
Previous Mer patches...
git merge origin/mer/libtool git merge origin/mer/obs-fix
(up to date!)
Now we have a new release
editor ChangeLog git add ChangeLog git commit -m"2.20.1-mer1" git tag 2.20.1-mer1
And a new Mer release
git checkout --track origin/Mer git merge master editor debian/changelog git add debian/changelog git commit -m"Mer_2.20.1-mer1" git tag Mer_2.20.1-mer1
Now push
git push --all git push --tags
The resultant merge looks like this :
Read upwards to progress in time. Note how on the right is the 'upstream' branch tagged at 2.20.1 then you see the Mer patches being applied to master which is then merged into Mer. (There is slight complexity here since the upstream changed to the *real* upstream).
Working from Gitorious
This should be written to say "Clone this repository on gitorious" and then publish back there and then submit a pull request to Mer.
For core work:
Essentially
git clone git@gitorious.org:mer/$GPKG.git git checkout --track origin/Mer
determine which feature or branch needs work. Then:
git checkout --track origin/mer/<feature>
hack...
Ready to test? You need to make a local test branch based on Mer
git checkout Mer git checkout -b local git merge mer/<feature>
Build and test...
If this works OK then clean up your mer/<feature> branch... probably doing a --squash and push the branch to gitorious.