Enterprise Provisioning - Strategy Variations
(→Installation server at Internet) |
|||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
Now we can either read about [[Enterprise_Provisioning_-_Future_Prospects|future prospects for provisioning]] or move onward to [[Enterprise_Provisioning_Summary|provisioning summary]]. | Now we can either read about [[Enterprise_Provisioning_-_Future_Prospects|future prospects for provisioning]] or move onward to [[Enterprise_Provisioning_Summary|provisioning summary]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Power users]] | ||
Revision as of 12:31, 27 May 2010
Note: Following variations have not been tried out
Contents |
Pincode based bootstrapping
A variation of SMS based bootstrapping. Instead of using SMS, the user connects using the device to Installation server which prompts a pincode. Otherwise the process is identical.
Components
Identical with strategy "Indirect enrollment, SMS based bootstrapping"
Firewall rules
Identical with strategy "Indirect enrollment, SMS based bootstrapping"
Security considerations
- Requires using a fairly short pincode
Pros and cons
- + No SMS gateway needed
- - Tedious to user since they still need to key in Installation server URL and the pin code
- - As laborious to implement as "Indirect enrollment, SMS based bootstrapping" strategy
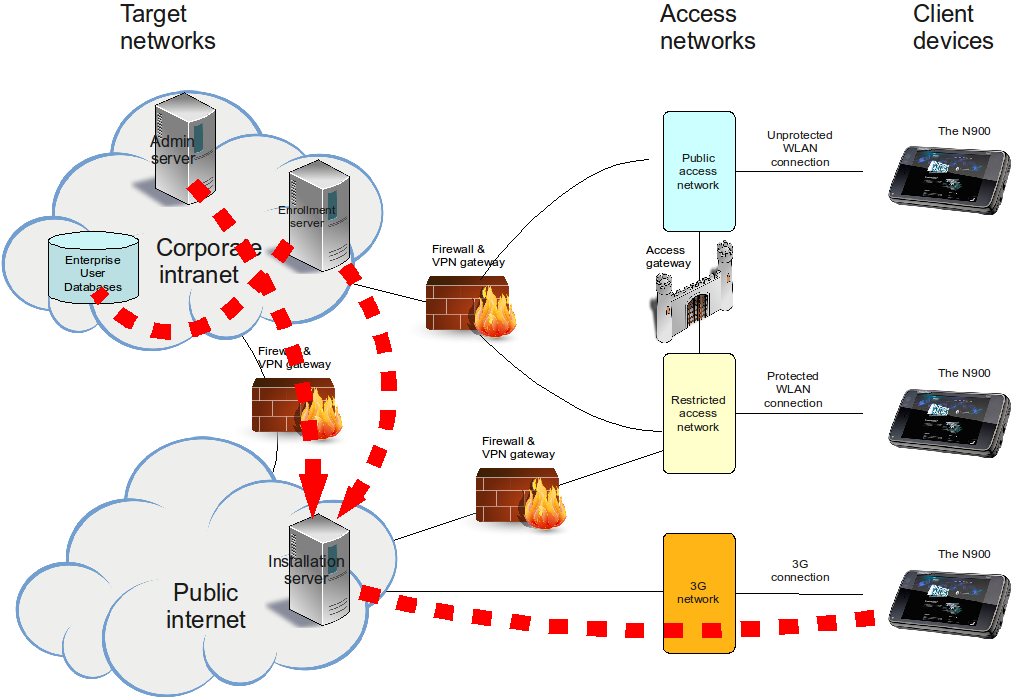
Installation server at Internet
The installation server could also be located in the public Internet. We present this alternative as a variation of the "Indirect enrollment, SMS based bootstrapping" strategy, since that is probably the most secure one.
Feasibility of this strategy likely requires flat 3G data transfer rates.
The process
Identical with the "Indirect enrollment, SMS based bootstrapping" strategy, but step 1 is not needed.
Components
Identical with "Indirect enrollment, SMS based bootstrapping" strategy.
Firewall rules
Identical with "Indirect enrollment, SMS based bootstrapping" strategy.
Security considerations
- SMS pincode can be set very long, and it is delivered using entirely different network than where it is used. No additional security considerations foreseen here.
- The biggest security risk is the server being compromised. Servers facing public Internet are under constant attack. They have to be properly hardened and managed professionally
- Likely, this option becomes feasible only in cases there is already a Internet-facing hardened and well-managed server at disposal
Pros and cons
- + Very simple to use. As close to "single click install" as it can get
- + Usable practically everywhere, including remote sites
- - Probably slow
- - Data transfer rates
Summary
Now we can either read about future prospects for provisioning or move onward to provisioning summary.