Changing the eMMC filesystem
(wikify slightly, add <code>, add link, remove table column width formatting, categorise) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Each filesystem got its own pros and cons. There is no 'one size fits all' type of filesystem; only filesystems each with their own use-cases. Therefore: do some extensive research before deciding to change your filesystem! | Each filesystem got its own pros and cons. There is no 'one size fits all' type of filesystem; only filesystems each with their own use-cases. Therefore: do some extensive research before deciding to change your filesystem! | ||
| - | This wiki page is focused on changing the filesystem of the /home partition. | + | This wiki page is focused on changing the filesystem of the <code>/home</code> partition. |
Prerequisites: | Prerequisites: | ||
| - | *The kernel you're running should support the filesystem you want to use. Either use kernel-power or compile a kernel yourself. | + | *The kernel you're running should support the filesystem you want to use. Either use [[Kernel Power|kernel-power]] or compile a kernel yourself. |
*Willingness to mess with Maemo's boot process (reflash risk!) | *Willingness to mess with Maemo's boot process (reflash risk!) | ||
== How to do it == | == How to do it == | ||
| - | Basically, you need to move /home to a temporary location, reformat its original partition with the filesystem of your choice, copy /home back and finally edit /etc/event.d/rcS-late. This can be a challenge as Maemo gets into a reboot loop when /home can't be mounted. Back up all your data! | + | Basically, you need to move <code>/home</code> to a temporary location, reformat its original partition with the filesystem of your choice, copy <code>/home</code> back and finally edit <code>/etc/event.d/rcS-late</code>. This can be a challenge as Maemo gets into a reboot loop when <code>/home</code> can't be mounted. Back up all your data! |
=== Solution #1: Do everything on-device === | === Solution #1: Do everything on-device === | ||
This solution is based on Solution #7 in [[Repartitioning_the_flash]]. | This solution is based on Solution #7 in [[Repartitioning_the_flash]]. | ||
| - | + | <ol> | |
| - | + | <li> | |
| - | + | Move <code>/home</code> as described in Solution #7 in [[Repartitioning_the_flash]]. Follow the described steps strictly until you reach the command which would actually repartition the flash (the sfdisk command). You don't need to follow any other steps from the mentioned solution from now onwards. | |
| - | + | </li> | |
| - | + | <li> | |
| - | + | Assuming you've successfully moved <code>/home</code> (e.g. you got a fully booted phone with <code>/home</code> on a different partition), format <code>/home</code> its original partition to your filesystem of choice and mount it. For example: | |
| - | + | <pre> | |
| - | + | mkfs.ext4 /dev/mmcblk0p2 | |
| - | + | mount -t ext4 -o rw,noatime,commit=1,data=writeback /dev/mmcblk0p2 /mnt | |
| - | + | </pre> | |
| - | Don't forget to unmount /home/user/MyDocs prior to copying! | + | </li> |
| - | + | <li> | |
| - | + | Copy your <code>/home</code> back to (now its reformatted) original partition: | |
| - | + | <pre> | |
| - | + | cp -a /home/* /mnt | |
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | Don't forget to unmount <code>/home/user/MyDocs</code> prior to copying! | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | <li> | ||
| + | Now you should edit <code>/etc/rcS-late</code> to make Maemo use <code>/home</code> its original partition again and accept its new filesystem type. | ||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li> | ||
| + | ''Making Maemo use <code>/home</code> its original partition again'' | ||
In step 1, you've added the line: | In step 1, you've added the line: | ||
| - | + | <pre> | |
| - | to /etc/event.d/rcS-late. Modify this line to represent the fstab entry of your new filesystem on /home its original partition. Examples include: | + | echo "/dev/mmcblk1p1 /home ext3 rw,noatime,errors=continue,commit=1,data=writeback 0 0" >> $tmp_fstab |
| - | + | </pre> | |
| - | + | to <code>/etc/event.d/rcS-late</code>. Modify this line to represent the fstab entry of your new filesystem on /home its original partition. Examples include: | |
| - | + | <pre> | |
| - | + | #ext4 example | |
| - | + | echo "/dev/mmcblk0p2 /home ext4 rw,noatime,errors=continue,commit=1,data=writeback 0 0" >> $tmp_fstab | |
| - | + | </pre> | |
| - | + | <pre> | |
| + | #Reiser4 example | ||
| + | echo "/dev/mmcblk0p2 /home reiser4 rw,noatime 0 0" >> $tmp_fstab | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
Make sure you add no invalid mount options! Mount failure results in a reboot-loop. You can test the mount options by trying to mount the partition manually prior to making it permanent. | Make sure you add no invalid mount options! Mount failure results in a reboot-loop. You can test the mount options by trying to mount the partition manually prior to making it permanent. | ||
| - | + | </li> | |
| - | + | <li> | |
| + | ''Making Maemo accept the new filesystem type'' | ||
Line no. 13, 18, 23, 24 and 26 of rcS-late got "ext3" hard-coded in it. We need to edit these lines to represent our new filesystem. | Line no. 13, 18, 23, 24 and 26 of rcS-late got "ext3" hard-coded in it. We need to edit these lines to represent our new filesystem. | ||
Ext4 example: | Ext4 example: | ||
| - | + | <pre> | |
| - | + | ##Begin of snippet | |
| - | + | script | |
| - | + | #mount /home; fix ext4 and retry mounting if 1st attempt fails | |
| - | + | mount_home () | |
| - | + | { | |
| + | /bin/mount /home && grep -q "/home ext4 rw" /proc/mounts | ||
| + | if [ $? -eq 0 ] | ||
| + | then | ||
| + | return 0 | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | grep -q "/home ext4 ro" /proc/mounts | ||
if [ $? -eq 0 ] | if [ $? -eq 0 ] | ||
then | then | ||
| - | + | umount /home | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
fi | fi | ||
| - | } | + | HOME_DEV=`grep "/home ext4" /etc/fstab | cut -d' ' -f1` |
| - | + | fsck.ext4 -y $HOME_DEV >> /var/lib/fsck_ext4_home.log 2>&1 | |
| - | + | sync | |
| + | /bin/mount /home && grep -q "/home ext4 rw" /proc/mounts | ||
| + | return $? | ||
| + | fi | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | ##End of snippet | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
Make sure line 24 contains a valid fsck.X command. Try running the command with all its parameters manually before making it permanent. | Make sure line 24 contains a valid fsck.X command. Try running the command with all its parameters manually before making it permanent. | ||
| - | + | </li> | |
| - | + | </ol> | |
| + | </li> | ||
| + | <li> | ||
| + | Reboot your phone. You're done now. | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
== Some initial benchmarks == | == Some initial benchmarks == | ||
| Line 81: | Line 99: | ||
How the benchmarks were performed: Reflashed & repartitioned phone in offline mode, SSH over usb. Used script (first round out of five dismissed in the averaged result): | How the benchmarks were performed: Reflashed & repartitioned phone in offline mode, SSH over usb. Used script (first round out of five dismissed in the averaged result): | ||
| - | + | <source lang="bash"> | |
| - | + | #!/bin/sh | |
| - | + | for run in `seq 1 5` | |
| - | + | do | |
| - | + | sync | |
| - | + | echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches | |
| - | + | sleep 1 | |
| - | + | time sh -c "cp [FILE/DIRECTORY] /mnt && sync" | |
| - | + | done | |
| - | + | ||
| - | The files were copied from /dev/mmcblk0p1 (FS: reiser4, LZO compression) to /dev/mmcblk0p2 (FS: depends on test) | + | df | grep /mnt |
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The files were copied from <code>/dev/mmcblk0p1</code> (FS: reiser4, LZO compression) to <code>/dev/mmcblk0p2</code> (FS: depends on test) | ||
Used ext3 options: | Used ext3 options: | ||
| - | + | mkfs.ext3 /dev/mmcblk0p2 | |
| - | + | mount -t ext3 -o rw,noatime,errors=continue,commit=1,data=writeback /dev/mmcblk0p2 /mnt | |
Used ext4 options: | Used ext4 options: | ||
| - | + | mkfs.ext4 /dev/mmcblk0p2 | |
| - | + | mount -t ext4 -o rw,noatime,errors=continue,commit=1,data=writeback /dev/mmcblk0p2 /mnt | |
Used reiser4 options: | Used reiser4 options: | ||
| - | + | mkfs.reiser4 -o create=ccreg40,compress=lzo1,cluster=8K,formatting=smart /dev/mmcblk0p2 | |
| - | + | mount -t reiser4 -o noatime /dev/mmcblk0p2 /mnt | |
Averaged values of the "real time" as reported by time | Averaged values of the "real time" as reported by time | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| - | ! | + | ! Filesystem |
| - | ! | + | ! linux-2.6.28.tar.bz2 @ 50.2MiB |
| - | ! | + | ! 500 (mostly text) files @ 4MiB |
| - | ! | + | ! 83 (mostly text) files @ 14.6MiB |
|- | |- | ||
|Ext3|| 14.3725s || 7.205s || 7.1025s | |Ext3|| 14.3725s || 7.205s || 7.1025s | ||
| Line 122: | Line 142: | ||
Space reported by df after each benchmark (in total 747264 1K blocks available) | Space reported by df after each benchmark (in total 747264 1K blocks available) | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| - | ! | + | ! Filesystem |
| - | ! | + | ! linux-2.6.28.tar.bz2 @ 50.2MiB |
| - | ! | + | ! 500 (mostly text) files @ 4MiB |
| - | ! | + | ! 83 (mostly text) files @ 14.6MiB |
|- | |- | ||
|Ext3|| 68668 (9%) || 22748 (3%) || 32368 (4%) | |Ext3|| 68668 (9%) || 22748 (3%) || 32368 (4%) | ||
| Line 138: | Line 158: | ||
== Different filesystem in action == | == Different filesystem in action == | ||
[[Image:screenshot_reiser4.png|Reiser4 in action]] | [[Image:screenshot_reiser4.png|Reiser4 in action]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:N900]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Power users]] | ||
Revision as of 13:30, 11 April 2011
As with most computers, the speed of the N900's internal storage often poses a bottleneck, slowing down the device during heavy reads/writes. Changing the filesystem can mitigate the impact of this.
By choosing an appropriate filesystem for the content of your disk, you are able to speed things up. Vice versa, a bad filesystem choice can negatively impact performance. A different reason to switch filesystems besides performance reasons can be because of the feature set offered by different filesystems. For example, ext3 is considered mostly as a very stable filesystem while Reiser4 offers transparent compression.
Each filesystem got its own pros and cons. There is no 'one size fits all' type of filesystem; only filesystems each with their own use-cases. Therefore: do some extensive research before deciding to change your filesystem!
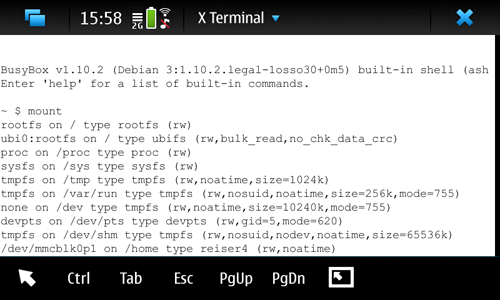
This wiki page is focused on changing the filesystem of the /home partition.
Prerequisites:
- The kernel you're running should support the filesystem you want to use. Either use kernel-power or compile a kernel yourself.
- Willingness to mess with Maemo's boot process (reflash risk!)
Contents |
How to do it
Basically, you need to move /home to a temporary location, reformat its original partition with the filesystem of your choice, copy /home back and finally edit /etc/event.d/rcS-late. This can be a challenge as Maemo gets into a reboot loop when /home can't be mounted. Back up all your data!
Solution #1: Do everything on-device
This solution is based on Solution #7 in Repartitioning_the_flash.
-
Move
/homeas described in Solution #7 in Repartitioning_the_flash. Follow the described steps strictly until you reach the command which would actually repartition the flash (the sfdisk command). You don't need to follow any other steps from the mentioned solution from now onwards. -
Assuming you've successfully moved
/home(e.g. you got a fully booted phone with/homeon a different partition), format/homeits original partition to your filesystem of choice and mount it. For example:mkfs.ext4 /dev/mmcblk0p2 mount -t ext4 -o rw,noatime,commit=1,data=writeback /dev/mmcblk0p2 /mnt
-
Copy your
/homeback to (now its reformatted) original partition:cp -a /home/* /mnt
Don't forget to unmount
/home/user/MyDocsprior to copying! -
Now you should edit
/etc/rcS-lateto make Maemo use/homeits original partition again and accept its new filesystem type.-
Making Maemo use
/homeits original partition again In step 1, you've added the line:echo "/dev/mmcblk1p1 /home ext3 rw,noatime,errors=continue,commit=1,data=writeback 0 0" >> $tmp_fstab
to
/etc/event.d/rcS-late. Modify this line to represent the fstab entry of your new filesystem on /home its original partition. Examples include:#ext4 example echo "/dev/mmcblk0p2 /home ext4 rw,noatime,errors=continue,commit=1,data=writeback 0 0" >> $tmp_fstab
#Reiser4 example echo "/dev/mmcblk0p2 /home reiser4 rw,noatime 0 0" >> $tmp_fstab
Make sure you add no invalid mount options! Mount failure results in a reboot-loop. You can test the mount options by trying to mount the partition manually prior to making it permanent.
-
Making Maemo accept the new filesystem type
Line no. 13, 18, 23, 24 and 26 of rcS-late got "ext3" hard-coded in it. We need to edit these lines to represent our new filesystem.
Ext4 example:
##Begin of snippet script #mount /home; fix ext4 and retry mounting if 1st attempt fails mount_home () { /bin/mount /home && grep -q "/home ext4 rw" /proc/mounts if [ $? -eq 0 ] then return 0 else grep -q "/home ext4 ro" /proc/mounts if [ $? -eq 0 ] then umount /home fi HOME_DEV=`grep "/home ext4" /etc/fstab | cut -d' ' -f1` fsck.ext4 -y $HOME_DEV >> /var/lib/fsck_ext4_home.log 2>&1 sync /bin/mount /home && grep -q "/home ext4 rw" /proc/mounts return $? fi } ##End of snippetMake sure line 24 contains a valid fsck.X command. Try running the command with all its parameters manually before making it permanent.
-
Making Maemo use
- Reboot your phone. You're done now.
Some initial benchmarks
Note from author: The benchmarks below are pretty limited, feel free to substitute them with more extended/reliable ones.
How the benchmarks were performed: Reflashed & repartitioned phone in offline mode, SSH over usb. Used script (first round out of five dismissed in the averaged result):
#!/bin/sh for run in `seq 1 5` do sync echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches sleep 1 time sh -c "cp [FILE/DIRECTORY] /mnt && sync" done df | grep /mnt
The files were copied from /dev/mmcblk0p1 (FS: reiser4, LZO compression) to /dev/mmcblk0p2 (FS: depends on test)
Used ext3 options:
mkfs.ext3 /dev/mmcblk0p2 mount -t ext3 -o rw,noatime,errors=continue,commit=1,data=writeback /dev/mmcblk0p2 /mnt
Used ext4 options:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/mmcblk0p2 mount -t ext4 -o rw,noatime,errors=continue,commit=1,data=writeback /dev/mmcblk0p2 /mnt
Used reiser4 options:
mkfs.reiser4 -o create=ccreg40,compress=lzo1,cluster=8K,formatting=smart /dev/mmcblk0p2 mount -t reiser4 -o noatime /dev/mmcblk0p2 /mnt
Averaged values of the "real time" as reported by time
| Filesystem | linux-2.6.28.tar.bz2 @ 50.2MiB | 500 (mostly text) files @ 4MiB | 83 (mostly text) files @ 14.6MiB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ext3 | 14.3725s | 7.205s | 7.1025s |
| Ext4 | 9.9725s | 7.115s | 6.1625s |
| Reiser4 | 10.015s | 5.6625s | 5.365s |
Space reported by df after each benchmark (in total 747264 1K blocks available)
| Filesystem | linux-2.6.28.tar.bz2 @ 50.2MiB | 500 (mostly text) files @ 4MiB | 83 (mostly text) files @ 14.6MiB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ext3 | 68668 (9%) | 22748 (3%) | 32368 (4%) |
| Ext4 | 68592 (9%) | 22700 (3%) | 32292 (4%) |
| Reiser4 | 51568 (7%) | 2420 (0%) | 13500 (2%) |
Do note that both Maemo and kernel-power lack Reiser4 support; you'll have to compile a kernel with Reiser4 support and reiser4progs yourself.