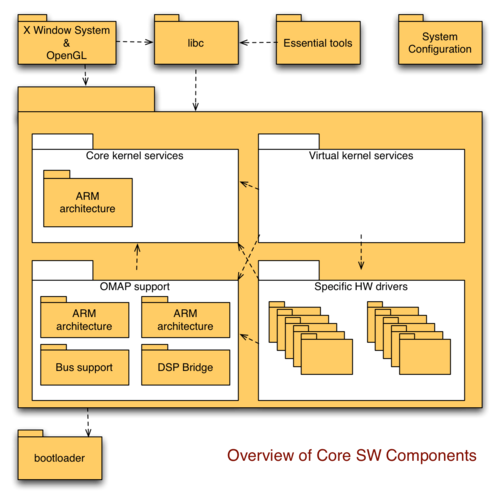
Documentation/Maemo 5 Developer Guide/Architecture/Core Domain
Contents |
[edit] Nolo bootloader
- Name
- NoLo (Nokia Loader)
- Purpose
- The bootloader does basic configuration of the HW, loads the kernel into memory, and passes control to the kernel. In addition to this basic task the NoLo boot loader has many features to support R&D. (The capability to flash the device is currently implemented in NoLo but it will become an R&D feature once flashing is moved to user space.)
- Responsibilities
-
- Load kernel into memory
- Initialize HW so that kernel is able to boot
- Pass ATAGs to the kernel and transfer execution to the kernel
- Production line flashing functionality
- Creates partitions
- Package / License
- nolo / Nokia
[edit] Linux Kernel
- Purpose
- The function of the kernel code is to provide all the basic services and hardware interfaces of the Linux operating system for the underlying programs. The kernel also passes the control to the chosen user space program (usually
/sbin/init) after initializing its own structures and drivers. When the kernel starts up, it checks a lot of the available subsystems and initializes everything according to the kernel configuration chosen at compile time. Some subsystems will be left uninitialized by the boot loader, for example, the display subsystem. - Responsibilities
- The operating system kernel
- Notes
- Maemo specific functionality is in OMAP3 & Rover HW specific code. OMAP3 support is developed, generally speaking, in the linux-omap tree, from which code is pulled into Maemo kernel.
- Package / License
- kernel / GPL2
- Public interfaces provided
- Linux kernel API: Linux system calls accessed through the C library
[edit] Kernel core services
- Purpose
- The Linux core services comprise generic, hardware independent code.
- Responsibilities
-
- memory management
- process management
- device management
- inter-process communication…
- Notes
- Used as is.
- Package / License
- kernel / GPL2
[edit] ARM architecture support
- Purpose
- The ARM architecture subsystem in the kernel provides mainly ARM specific implementations of necessary core mechanisms.
- Responsibilities
- ARM specific implementations of kernel mechanisms.
- Notes
- Used as is.
- Package / License
- kernel / GPL2
[edit] Kernel framework
- Purpose
- The low level HW drivers provide the concrete implementation that is bound to the virtual services in the Linux kernel to provide the complete functionality.
- Responsibilities
-
- ALSA & Video for Linux 2 (V4L2) APIs,Networking stack, BlueZ (Bluetooth), mac80211 (WLAN), USB core
- Virtual File System, file systems, block devices, MTD
- Frame buffer, serial port, input layer (keyboard, touch screen)
- Package / License
- kernel / GPL2
- Public interfaces provided
-
- ALSA: Advanced Linux Sound Architecture, de facto Linux sound API.
- V4L2: Video for Linux 2, de facto video capture API + Maemo specific ioctls
- Camera ioctls: Extensions to V4L2 interface used by the camera daemon.
- File systems: FAT16/32, EXT3 and UBIFS file systems are currently supported on the platform.
- Frame buffer: The raw frame buffer interface is used in early stages of the boot.
- Input layer: The input layer events are routed via X to applications.
- Serial port: Available for R&D use.
[edit] OMAP3 support
- Purpose
- OMAP specific code implements the device drivers and bus support for the specific hardware included in the OMAP3430 chip. The supported OMAP3 subsystems are described in the following subsections.
- Responsibilities
-
- DMA: OMAP3 has a 32 channel general purpose DMA controller, display DMA, HS USB DMA, and IVA 2.2 DMA (not supported).
- Interrupt handling:OMAP3 has an interrupt controller (MPU INTC) with 96 synchronous interrupt lines.
- OMAP3 specific power management functionality: The power management functionality is built on top of idle, sleep, suspend, resume, and dynamic voltage & frequency scaling functionalities [SystemSW].
- DSP Bridge, ioMMU, OMAP watchdog, GPIOs, timers, Muxing framework
- Gpmc (OneNAND driver), hsmmc (MMC/SD)
- Bus drivers: spi, i2c, McBSP, uart, SSI
- Package / License
- kernel / GPL2
[edit] DSP Bridge
- Purpose
- OMAP's integrated DSP allows offloading tasks to the DSP from the ARM processor. This is exposed with the DSP bridge component.
- Responsibilities
- Interface to the OMAP3’s DSP which is used for codec acceleration.
- Package / License
- kernel / GPL2
[edit] OMAP3 bus drivers
- Responsibilities
- Drivers for the following buses: SPI, SSI, McBSP, GPIOs, HS MMC/SD, UART, I2C/I2S, RFBI, CBUS, Flash BUS, (STI/XTI debugging interfaces)
- Package / License
- kernel / GPL2
[edit] OMAP3 specific HW drivers
- Responsibilities
- Drivers for following HW components:SGX, OMAP framebuffer & LCD & TV-out, Camera & ISP, HS USB Host & HS USB OTG, SDRAM memory controller, GPMC NAND/NOR flash&SRAM controller, and PRCM
- Package / License
- kernel / GPL2
[edit] Specific hardware drivers
- Responsibilities
- The following components external to OMAP are supported: USB transceiver, USB charging, FM RX/TX, WLAN, OneNAND flash, touch screen, audio, stereo IHF, earphone, digital mics, LEDs, HW keys, ALS, Accelerometer, Vibrator, Proximity sensor, Miscellaneous Sensors, LCD backlight, Bluetooth, WLAN, CMT, Ethernet (R&D use).
- Package / License
- kernel / GPL2
[edit] X Window System
- Purpose
- Graphical User Interface framework
- Responsibilities
-
- XServer – GUI framework & resource management
- Xv – Video playback interface
- XRandR – Support for rotation & output configuration
- XRender, XComposite – Support for composited UI
- XInput – Routing of input events to applications
- Package/ License
- Several/ MIT
- Public interfaces provided
-
- X protocol: Interface to the X window system
- DRI2: Direct Rendering Infrastructure 2, OpenGL ES 2.0
[edit] OpenGL ES 2.0
- Purpose
- Accelerated 3D rendering
- Responsibilities
-
- Accelerated 3D rendering
- Acceleration of XRender
- Notes
- The user space GLES components are licensed from Imagination.
- Package/ License
- opengles2-sgx-img-common, libgles2(-sgx-img/-sgx-img) / Nokia
- Public interfaces provided
- EGL: Khronos API for OpenGL ES application for interacting with the native graphics framework.
[edit] C library
- Purpose
- Posix C library functionality
- Responsibilities
-
- System call interfaces
- Posix functionalities
- Package/ License
- glibc / LGPL2
[edit] Essential tools
- Purpose
- The essential tools provide tools needed in system scripts. The role is similar to the Debian essentials (tools that are always installed in a Debian system).
- Responsibilities
- system tools like: shell, grep, find, dpkg, …
- Notes
- Many tools have many limitations compared to the Debian versions. Not all Debian essentials are supported.
- Package/ License
- busybox / GPL2
- Public interfaces provided
-
- Posix shell
- Subset of Debian essentials
[edit] Sysinfod
- Purpose
- Provide interface for accessing device information
- Responsibilities
- Provide a D-Bus interface to device specific information (HW id, WLAN MAC, …)
- Package / License
- sysinfod / Nokia
- Public interface provided
- Sysinfod D-Bus interface
[edit] Softupd
- Purpose
- Program for flashing the eMMC contents
- Responsibilities
-
- Unpacks a FIASCO image fed to it
- Copies the unpacked contents to eMMC
- Package / License
- softupd / Nokia
[edit] Fiasco-flasher
- Purpose
- Tool for updating the kernel flashed to the device
- Responsibilities
-
- Flash kernel image into the kernel partition
- Reboot the device
- Package / License
- fiasco-flasher / Nokia
- Public interface provided
- Fiasco-flasher: The tool can be used to flash a new kernel image into the kernel partition.
- This page was last modified on 7 September 2010, at 11:18.
- This page has been accessed 33,506 times.